REACH3 Primary Endpoint: ORR at Week 241,a
ORR Through Week 242,c

aORR was defined as the proportion of patients with CR or PR at week 24, according to 2014 NIH consensus criteria.1
bOne-sided P value, OR, and 95% CI were calculated using stratified Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel test, stratifying for moderate and severe cGVHD.1
cDefined as the proportion of patients who achieved CR or PR through week 24 (cycle 7, day 1), according to 2014 NIH consensus criteria.2

If I don’t see at least some response within the first week or I am unable to taper steroid use, I intervene with Jakafi as opposed to taking the chance that the disease could become more severe.
Karolina Faysman, MSN, AOCNP, GVHD Expert
Patients treated with Jakafi were
3×
more likely to achieve an overall response at week 24 vs BAT (OR, 2.99)1
Median time to first response
3
weeks (range: 2-24) with Jakafi and 4 weeks (range: 2-25) with BAT2
- 74% of patients treated with BAT received ECP, MMF, or ibrutinib; ORR at week 24 was1*†:
- ECP: 29.1% (16/55; CR, 1.8%; PR, 27.3%), MMF: 28.6% (10/35; CR, 2.9%; PR, 25.7%), ibrutinib: 22.2% (6/27; CR, 7.4%; PR, 14.8%)3
*The 74% value is based on the number of patients treated with BAT (n=158). ORRs for the remaining BATs were 20% (1/5) for everolimus, 25% (2/8) for imatinib, 20% (1/5) for infliximab, 30% (3/10) for low-dose MTX, 16.7% (1/6) for rituximab, and 28.6% (2/7) for sirolimus.1,3
†REACH3 was not powered to compare ORR for Jakafi to individual BATs.
Study design
REACH31,2

aCrossover from BAT to Jakafi was permitted on or after week 24 if patients progressed, had a mixed or unchanged response, developed toxicity to BAT, or experienced a cGVHD flare. 61 patients crossed over to Jakafi after week 24. 72% of those who crossed over remained on Jakafi longer than 24 weeks.1,4
bBAT was chosen by the investigator prior to randomization: Options included ibrutinib, ECP, low-dose MTX, MMF, rituximab, everolimus, sirolimus, imatinib, infliximab, and pentostatin.2
cDefined as the proportion of patients with CR or PR at week 24.1
dDefined as the earliest time from date of randomization to relapse or recurrence of underlying disease or death due to underlying disease, nonrelapse mortality, or addition or initiation of another systemic therapy for cGVHD.1
eDefined as a ≥7-point reduction from baseline in total symptom score on the mLSS, which measures the symptoms of cGVHD on a scale of 0 to 100, with higher scores indicating worse symptoms.1
- Inclusion criteria1*
- Age 12 and older
- Allogeneic stem cell transplant from any donor source and donor type
- SR/SD cGVHD per NIH consensus criteria (moderate or severe)
- Evident myeloid and platelet engraftment
- In the Jakafi Prescribing Information, efficacy was based on ORR through week 24 (cycle 7, day 1)2
*Organ involvement at baseline for all patients (N=329): skin (71.1%), mouth (60.8%), eyes (57.4%), lungs (42.9%), joints and fascia (27.4%), liver (24.9%), GI tract (22.8%), genital tract (9.4%), missing (0.3%). Organ involvement was based on NIH consensus staging criteria at screening. A score of ≥1 was counted as organ involvement. Patients with missing assessments of single organs were counted as having no organ involvement for the organ assessed.1
BAT=best available therapy; BID=twice daily; cGVHD=chronic graft-versus-host disease; CNI=calcineurin inhibitor; CR=complete response; ECP=extracorporeal photopheresis; FFS=failure-free survival; GI=gastrointestinal; mLSS=modified Lee Symptom Scale; MMF=mycophenolate mofetil; MTX=methotrexate; NIH=National Institutes of Health; ORR=overall response rate; PR=partial response; REACH=Ruxolitinib in patiEnts with refrACtory graft-versus-Host disease after allogeneic stem cell transplantation; SD=steroid-dependent; SR=steroid-refractory.
REACH3: ORRs at Week 24 With Jakafi and Individual BATs1


- REACH3 was not powered to compare ORR for Jakafi to individual BATs
- 74% of patients on BAT received ECP, MMF, or ibrutinib1*
*BAT was chosen by the investigator at the time of randomization.2

[Another primary goal] is to help prevent disease progression by keeping patients on an effective therapy for ongoing response to treatment. This is why we again turn to Jakafi. While we assess the benefits of treatment versus the risks in each patient, we believe that intervening early with Jakafi is important.
Preet M. Chaudhary, MD, PhD, GVHD Expert
Overall Response at Week 24 by Time-to-Treat Initiation From SR Diagnosis5,a
aNo significant differences were observed between ruxolitinib time-to-treatment subgroups for ORR, BOR, or DOR.5
My experience has taught me the importance of early intervention on second-line therapy. This is supported by the REACH3 data.
Haris Ali, MD, GVHD Expert

REACH3 Subgroup Analysis: ORR by Baseline Disease Severity at Week 241,4

When managing our patients, we do not delay treatment. We take an aggressive approach and intervene with Jakafi at the first signs of initial treatment failure to not let cGVHD smolder over time.
Preet M. Chaudhary, MD, PhD, GVHD Expert
REACH3 Subgroup Analysis: ORR at Week 24 by Baseline Organ Involvement1,a
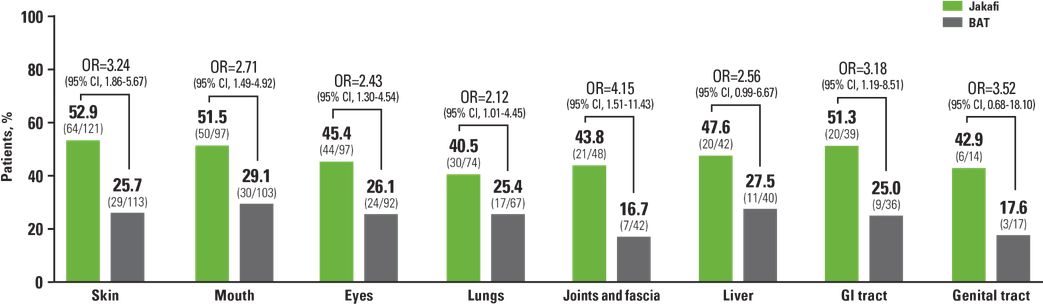

aPatients with >1 affected organ were counted in each organ subgroup. Organ involvement was defined as organ score ≥1 based on the cGVHD staging criteria.1

Seeing that Jakafi is effective across the board regardless of the organs involved gives us the confidence to initiate Jakafi at early changes in skin disease to really get the opportunity to help control cGVHD.
Preet M. Chaudhary, MD, PhD, GVHD Expert
REACH3 Key Secondary Endpoint: Kaplan-Meier Analysis of DOR4,6
*DOR was defined as the time from first response until cGVHD progression, death, or the date of change/addition of systemic therapies for cGVHD.5
Estimated probability of maintaining DOR
At 12 months:
70.2%
with Jakafi (95% CI, 61.4-77.5) vs 39.8% with BAT (95% CI, 30.4-49.1)4,6
At 36 months:
59.6%
with Jakafi (95% CI, 50.4-67.6) vs 26.7% with BAT (95% CI, 18.5-35.5)4,6
- Median DOR was not reached with Jakafi vs 6.4 months with BAT6
- Patients who crossed over from BAT to Jakafi still had significant response rates. Additionally, after crossover, disease progression occurred in only 1 patient6
- In the primary analysis, estimated probability of maintaining response to therapy at 12 months was 68.5% with Jakafi (95% CI: 58.9-76.3) and 40.3% with BAT (95% CI: 30.3-50.2)1

In my many years of experience, the responses demonstrated in the REACH3 trial align with what I’m seeing in my clinical practice.
Haris Ali, MD, GVHD Expert
REACH3 Key Secondary Endpoint: Kaplan-Meier Analysis of FFS4,6
*Defined as the earliest time from date of randomization to recurrence of underlying disease, start of new systemic treatment for cGVHD, or death, whichever came first.4
Estimated probability of FFS
At 12 months:
64%
with Jakafi (95% CI, 56.1-70.8) vs 28.8% with BAT (95% CI, 21.8-36.1)4,6
At 36 months:
56.5%
with Jakafi (95% CI, 48.5-63.7) vs 18.2% with BAT (95% CI, 12.5-24.9)4,6
- Median FFS was longer with Jakafi (38.4 months) vs BAT (5.7 months) (HR, 0.361; 95% CI, 0.268-0.485)6
- Median overall survival was not reached and there was no difference in risk of death between arms (HR, 0.851; 95% CI, 0.544-1.331)6
- In the primary analysis, estimated probability of FFS at 6 months was 74.9% with Jakafi (95% CI: 67.5-80.9) and 44.5% with BAT (95% CI: 36.5-52.1)1

I found it interesting to see the plateaus in the failure-free-survival and duration-of-response graphs, as they support my preference for keeping patients on Jakafi for an extended period with the hope that I can eventually taper them off.
Haris Ali, MD, GVHD Expert

BAT=best available therapy; BOR=best overall response; cGVHD=chronic graft-versus-host disease; CI=confidence interval; CR=complete response; DOR=duration of response; ECP=extracorporeal photopheresis; FFS=failure-free survival; GI=gastrointestinal; HR=hazard ratio; MMF=mycophenolate mofetil; MTX=methotrexate; NIH=National Institutes of Health; OR=odds ratio; ORR=overall response rate; PR=partial response; REACH=Ruxolitinib in patiEnts with refrACtory graft-versus-Host disease after allogeneic stem cell transplantation; SR=steroid refractory.
References: 1. Zeiser R, Polverelli N, Ram R, et al; for the REACH3 Investigators. Ruxolitinib for glucocorticoid-refractory chronic graft-versus-host disease. N Engl J Med. 2021;385(3):228-238. Supplementary appendix available at: https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2033122. 2. Jakafi Prescribing Information. Wilmington, DE: lncyte Corporation. 3. Locatelli F; for the REACH3 Study Group. Ruxolitinib vs best available therapy in patients with steroid-refractory/dependent chronic graft-vs-host disease: subgroup analyses of overall response rate in the phase 3 REACH3 trial. Presented at: 47th Annual Meeting of the EBMT; March 14-17. 2021; Rome, Italy. 4. Data on file. Incyte Corporation. Wilmington, DE. 5. Zeiser R, Xue Z, Bhatt V, Galvin J, Locatelli F. Early versus late treatment with ruxolitinib in patients with steroid-refractory chronic graft-versus-host disease: a post hoc analysis from the randomized, phase 3 REACH3 study. Poster presented at: 64th American Society of Hematology (ASH) Annual Meeting and Exposition; December 10-13, 2022; New Orleans, LA. 6. Zeiser R, Russo D, Ram R, et al. Ruxolitinib in patients with chronic graft-versus-host disease: 3-year final analysis of efficacy and safety from the phase III REACH3 study. Presented at: 65th American Society of Hematology Annual Meeting and Exposition; December 9-12, 2023; San Diego, CA. Session 722.







