Significantly more patients
Achieved complete hematologic remission with Jakafi® (ruxolitinib)
Patients on Jakafi demonstrated significantly higher rates of complete hematologic remission (CHR)* vs BAT1
Kaplan-Meier estimate: durability of CHR at 5 years
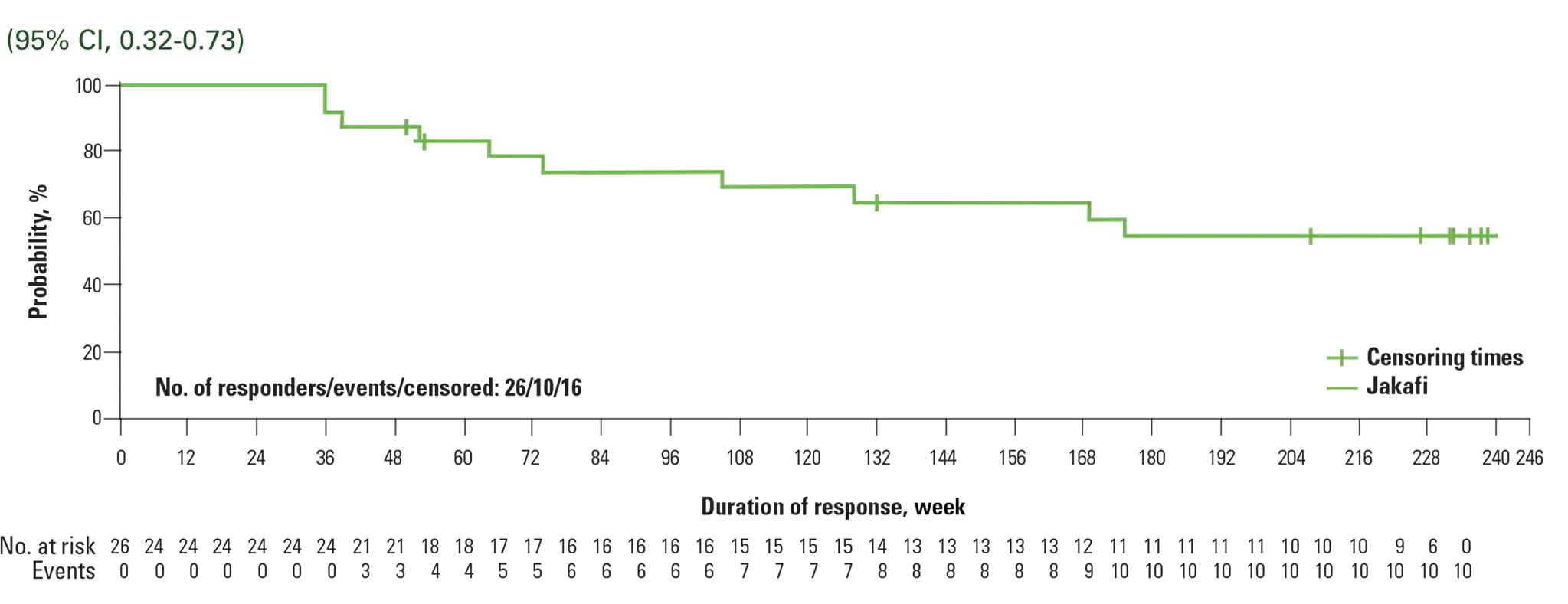
Reprinted from The Lancet Haematology, Vol 7, Kiladjian J-J, Zachee P, Hino M, et al, Long-term efficacy and safety of ruxolitinib versus best available therapy in polycythaemia vera (RESPONSE): 5-year follow up of a phase 3 study, e226-e237, Copyright 2020, with permission from Elsevier.
- Analysis was conducted in week 32 CHR responders, beginning at week 322
- Progression events for the evaluation of duration of CHR included first of 2 consecutive Hct assessments that confirmed phlebotomy eligibility, first of 2 contiguous visits during which platelet count was >400 × 109/L or WBC count was >10 × 109/L, death, or development of MF or acute leukemia3
Individual component of CHR
Jakafi reduced mean WBC counts

It’s important in patients with polycythemia vera to establish what their baseline white blood cell count is. Ideally, we want this number to be at or below 11,000 because we understand there’s some risk associated with a higher baseline white blood cell count.
Exploratory analyses from the RESPONSE trial: WBC count data

From The New England Journal of Medicine, Vannucchi AM, Kiladjian JJ, Griesshammer M, et al, Ruxolitinib versus standard therapy for the treatment of polycythemia vera, 372, 426-435. Copyright © 2015. Massachusetts Medical Society. Reprinted with permission from Massachusetts Medical Society.
- As shown below, data for patients treated with HU were included in the group of patients receiving BAT5
With WBC Counts ≥11 × 109/L5

Comprehensive haematological control with ruxolitinib in patients with polycythaemia vera resistant to or intolerant of hydroxycarbamide, Harrison CN, Griesshammer M, Miller C, et al. Copyright © 2018 John Wiley & Sons Ltd, British Journal of Haematology. Reproduced with permission of John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
- At baseline, 75.5% of patients (n=83) receiving Jakafi and 71.4% of patients (n=80) receiving BAT had WBC counts ≥11 × 109/L5
*CHR was defined as achieving Hct control (as specified in the primary endpoint), platelet count ≤400 × 109/L, and WBC count ≤10 × 109/L.1
†Jakafi: 95% CI, 0.16-0.33; BAT: 95% CI, 0.04-0.15.1
BAT=best available therapy; CI=confidence interval; Hct=hematocrit; HU=hydroxyurea; MF=myelofibrosis; MPN=myeloproliferative neoplasm; PV=polycythemia vera; RESPONSE=Randomized study of Efficacy and Safety in POlycythemia vera with JAK iNhibitor ruxolitinib verSus bEst available care; WBC=white blood cell.
References: 1. Jakafi [package insert]. Wilmington, DE: Incyte Corporation. 2. Kiladjian J-J, Zachee P, Hino M, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of ruxolitinib versus best available therapy in polycythaemia vera (RESPONSE): 5-year follow up of a phase 3 study. Lancet Haematol. 2020;7(3):e226-e237. Supplementary appendix available at: doi:10.1016/S2352-3026(19)30207-8. 3. Data on file. Incyte Corporation. Wilmington, DE. 4. Vannucchi AM, Kiladjian JJ, Griesshammer M, et al. Ruxolitinib versus standard therapy for the treatment of polycythemia vera. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(5):426-435. Supplementary appendix available at: https://www.nejm.org/doi/suppl/10.1056/NEJMoa1409002/suppl_file/nejmoa1409002_appendix.pdf. 5. Harrison CN, Griesshammer M, Miller C, et al. Comprehensive haematological control with ruxolitinib in patients with polycythaemia vera resistant to or intolerant of hydroxycarbamide. Br J Haematol. 2018;182(2):279-284. Supplemental information available at: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/bjh.14764.


